LDM Triple, Treatment
Effective Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Diabetic wounds, particularly diabetic foot ulcers, are a common and serious complication for individuals living with diabetes. These wounds typically result from a combination of factors, including poor circulation, neuropathy (nerve damage), and high blood sugar levels, which can impair the body’s natural healing process. In Dubai, where the prevalence of diabetes is notably high, awareness and early intervention are crucial in managing these wounds effectively. Diabetic wounds can range from minor cuts and blisters to severe ulcers that, if left untreated, may lead to serious infections and even amputation. Early detection and prompt treatment are essential to prevent these severe outcomes and ensure better health and quality of life for those affected.
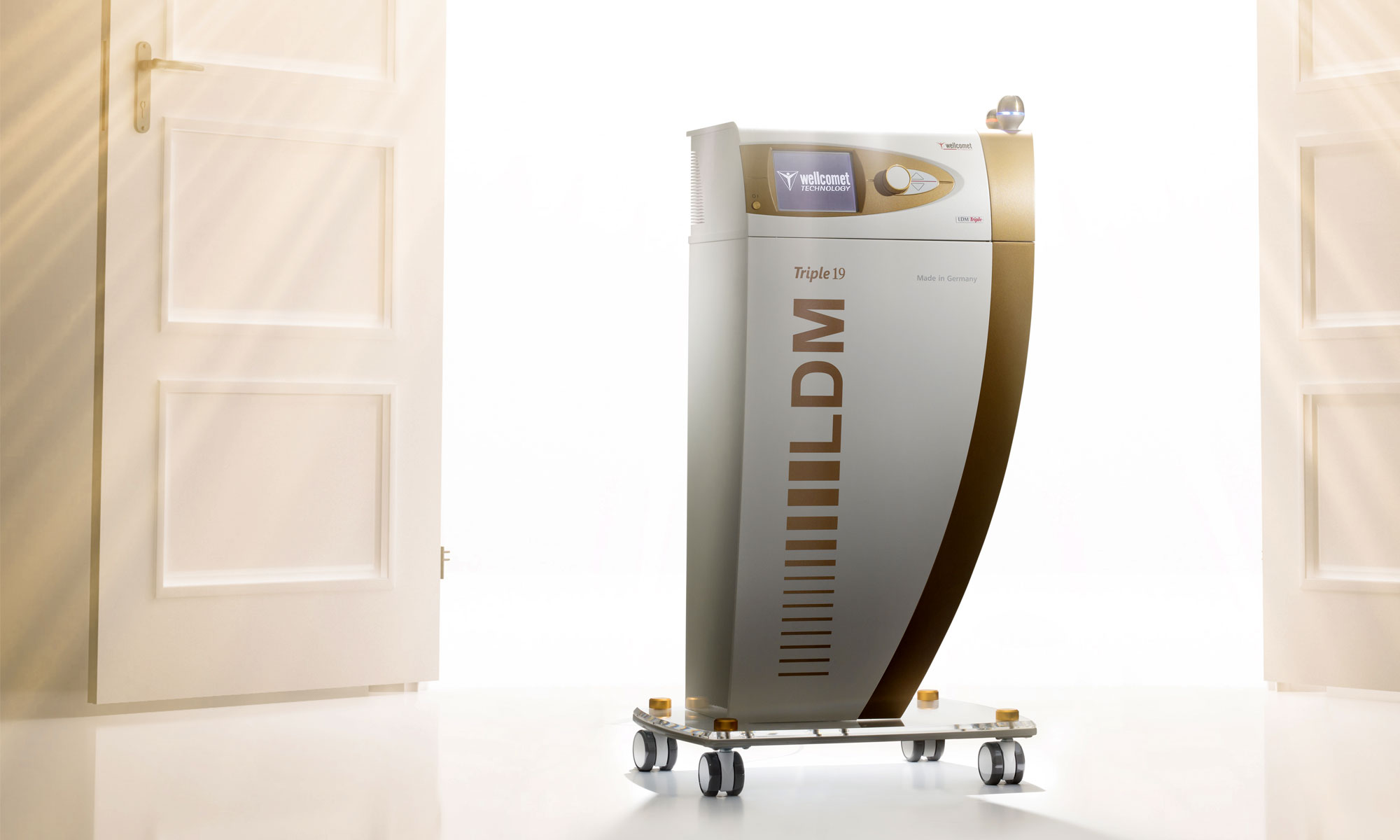
Wellcometme is committed to providing advanced and effective solutions for the treatment of diabetic wounds. One of the cutting-edge technologies we offer is the LDM MED Triple device, which uses innovative ultrasound waves to enhance wound healing. This device works by improving blood circulation, reducing inflammation, and stimulating tissue regeneration, making it an effective tool in the management of diabetic wounds. By incorporating the LDM MED Triple into comprehensive wound care plans, patients in Dubai can experience faster healing times and reduced risk of complications. Our goal is to support individuals with diabetes in achieving optimal health outcomes through state-of-the-art treatments and personalized care. If you or a loved one are dealing with diabetic wounds, our expert team is here to help guide you through effective treatment options to enhance healing and improve quality of life.
Causes and Risk Factors of Diabetic Wounds
Diabetic wounds, particularly those affecting the feet, are a significant concern for individuals with diabetes. These wounds can develop due to a variety of underlying causes and are often exacerbated by specific risk factors. Understanding these causes and risk factors is crucial for preventing the development of wounds and managing existing ones effectively. In Dubai, where diabetes prevalence is high, awareness and proactive management of these factors can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Causes of Diabetic Wounds
- Peripheral Neuropathy:
- Peripheral neuropathy, or nerve damage, is a common complication of diabetes. High blood sugar levels over time can damage the nerves, particularly in the extremities like the feet. This damage reduces sensation, making it difficult for individuals to feel pain or pressure. As a result, minor injuries or pressure points can go unnoticed and untreated, leading to the development of wounds.
- Poor Circulation:
- Diabetes can lead to poor circulation, particularly in the lower extremities. Reduced blood flow means less oxygen and fewer nutrients reach the tissues, impairing the body’s natural ability to heal wounds. This compromised circulation makes it easier for wounds to develop and harder for them to heal.
- Hyperglycemia:
- Consistently high blood sugar levels can impair the immune system and the body’s ability to fight infections. Hyperglycemia also affects the function of white blood cells, reducing their ability to respond to and clear infections. This makes even minor wounds susceptible to becoming chronic and infected.
- Immune System Impairment:
- Diabetes can weaken the immune system, making it more challenging for the body to combat infections. This weakened response can cause wounds to become infected more easily and can slow down the healing process.
Risk Factors for Diabetic Wounds
- Duration of Diabetes:
- The longer an individual has diabetes, the higher their risk of developing complications such as neuropathy and poor circulation, which contribute to the development of diabetic wounds.
- Poor Glycemic Control:
- Individuals who have difficulty maintaining stable blood sugar levels are at greater risk of developing wounds. Fluctuating blood sugar levels can exacerbate neuropathy and impair the immune system, leading to a higher likelihood of wound formation.
- Smoking:
- Smoking can further impair circulation and reduce the amount of oxygen in the blood. For individuals with diabetes, smoking increases the risk of developing peripheral artery disease, which can significantly worsen circulation and increase the risk of wounds.
- Obesity:
- Excess weight puts additional pressure on the feet, increasing the risk of blisters, calluses, and other minor injuries that can develop into serious wounds. Obesity is also associated with poorer glycemic control and increased inflammation, both of which contribute to the risk of wound development.
- Previous Foot Ulcers or Amputations:
- Individuals with a history of foot ulcers or amputations are at higher risk for developing new wounds. This is often due to the presence of underlying conditions such as neuropathy and poor circulation, which persist even after the initial wound has healed.
- Inadequate Foot Care:
- Poor foot hygiene and inadequate foot care practices can lead to the development of wounds. Regular inspection and care of the feet are essential for preventing injuries and catching potential problems early.
- Use of Inappropriate Footwear:
- Wearing ill-fitting shoes or shoes that do not provide adequate support can lead to blisters, calluses, and other foot injuries. These injuries can quickly become serious wounds in individuals with diabetes.
Preventive Measures and Management
Preventing diabetic wounds requires a multifaceted approach that includes maintaining good glycemic control, practicing proper foot care, and addressing lifestyle factors such as smoking cessation and weight management. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are crucial for early detection and management of potential issues.
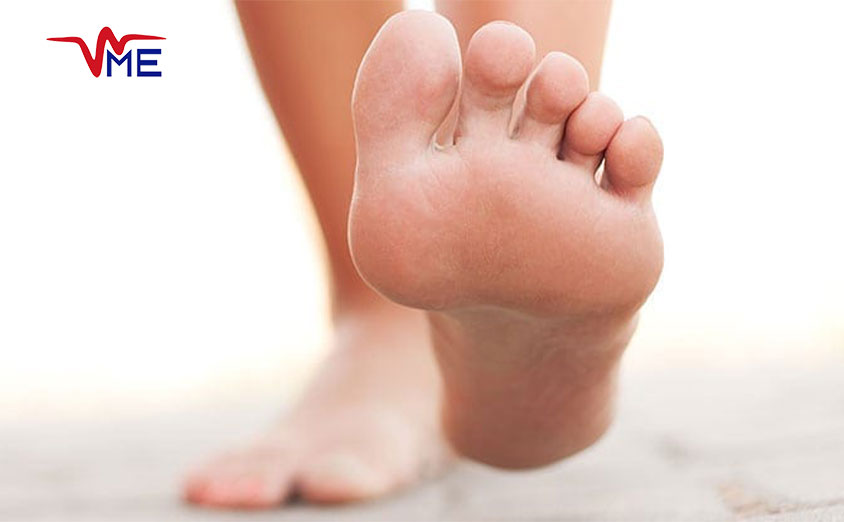

Symptoms and Warning Signs of Diabetic Wounds
Diabetic wounds, especially those affecting the feet, are a serious complication for individuals living with diabetes. Early detection and timely intervention are crucial to prevent these wounds from becoming severe and leading to further complications. Recognizing the symptoms and warning signs of diabetic wounds can make a significant difference in the management and outcome of these conditions. For residents of Dubai and the UAE, understanding these signs is vital given the high prevalence of diabetes in the region.
Common Symptoms of Diabetic Wounds
- Persistent Pain or Discomfort:
- Although individuals with diabetic neuropathy may experience reduced sensation, any persistent pain or discomfort in the feet or lower extremities should be taken seriously. Pain can be a sign of underlying issues such as infections or pressure ulcers developing.
- Visible Ulcers or Sores:
- One of the most obvious signs of a diabetic wound is the presence of open sores or ulcers on the feet. These ulcers can vary in size and depth and may appear on pressure points such as the ball of the foot, the heel, or between the toes.
- Swelling and Redness:
- Swelling and redness around a wound or in the lower extremities can indicate inflammation or infection. This is particularly concerning if it does not subside with rest or elevation of the affected limb.
- Drainage or Pus:
- Any discharge, including clear fluid, blood, or pus, from a wound should be addressed immediately. Drainage often indicates that the wound is not healing properly and may be infected.
- Foul Odor:
- A foul smell emanating from a wound is a strong indicator of infection. This should prompt immediate medical evaluation and treatment to prevent further complications.
- Skin Temperature Changes:
- A noticeable increase or decrease in skin temperature around the wound area can signify an underlying problem. Warmth might suggest inflammation or infection, while cooler skin could indicate poor blood flow.
- Calluses or Corns:
- Thickened skin areas, such as calluses or corns, can develop into ulcers if left untreated. These are often found on the soles of the feet and can mask underlying sores.
Warning Signs of Diabetic Wounds
- Numbness or Tingling:
- Diabetic neuropathy often leads to numbness or tingling sensations in the feet. While this can mask pain, it also means that injuries might go unnoticed, leading to the development of severe wounds.
- Cracked or Dry Skin:
- Diabetes can cause the skin to become dry and prone to cracking. These cracks can serve as entry points for bacteria, leading to infections and subsequent wound formation.
- Changes in Skin Color:
- Any changes in skin color, such as becoming pale, blue, or darkened, should be evaluated by a healthcare professional. These changes can indicate issues with blood flow or tissue health.
- Poor Nail Health:
- Thickened, brittle, or discolored toenails can be a sign of fungal infections or other underlying health issues. Infected nails can contribute to the development of wounds if not properly managed.
- Slow Healing of Minor Injuries:
- If minor cuts, blisters, or abrasions are slow to heal, this could be a sign of compromised blood flow and immune response. Slow healing is a hallmark of diabetic complications.
- Recurrent Infections:
- Frequent infections in the feet or lower extremities can indicate underlying problems with wound healing and immune function. Recurrent infections are a significant warning sign that requires medical attention.
Importance of Regular Foot Inspections
For individuals with diabetes, regular foot inspections are essential for early detection and prevention of diabetic wounds. Daily self-examinations can help identify potential problems before they become severe. It is important to look for any signs of redness, swelling, blisters, or changes in skin texture and color. Using a mirror or enlisting the help of a family member can ensure that all areas of the feet are thoroughly checked.
Types of Diabetic Wounds
Diabetic wounds are a serious concern for individuals living with diabetes, particularly due to their potential to develop into severe complications if not managed properly. Understanding the different types of diabetic wounds is crucial for effective prevention and treatment. In Dubai, where diabetes is prevalent, knowing these types can help in early detection and better management of the condition. Here, we discuss the most common types of diabetic wounds and their characteristics.
Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Diabetic foot ulcers are the most common type of diabetic wound. They typically occur on the bottom of the foot, often at pressure points such as the ball of the foot or the heel. These ulcers are caused by a combination of factors, including peripheral neuropathy, poor circulation, and pressure from ill-fitting shoes or prolonged standing. Diabetic foot ulcers can range from superficial to deep, and if left untreated, they can become infected and lead to serious complications, including amputation.
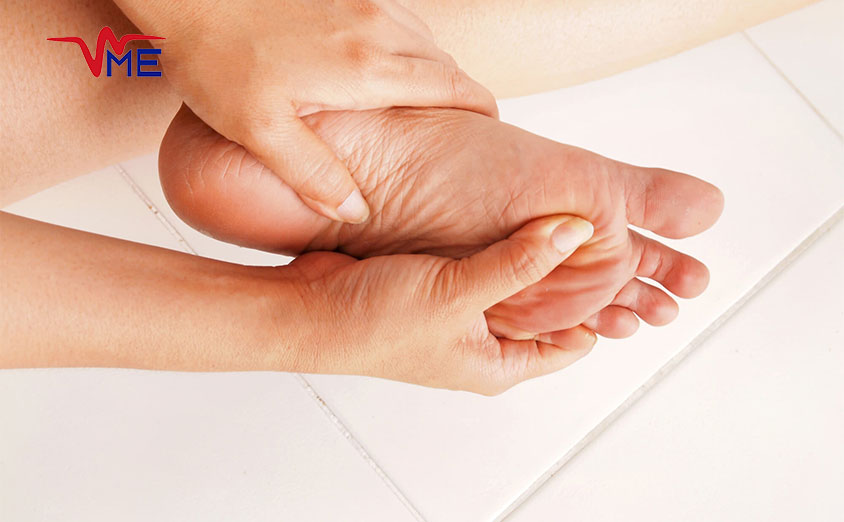
Neuropathic Ulcers
Neuropathic ulcers occur due to diabetic neuropathy, where nerve damage leads to a loss of sensation in the feet. Without pain to signal injury, minor cuts, blisters, or sores can go unnoticed and worsen over time. These ulcers usually appear on weight-bearing areas of the foot and can penetrate deep into the tissue, making them prone to infection. Regular foot inspections are vital for early detection and management of neuropathic ulcers.
Ischemic Ulcers
Ischemic ulcers are caused by poor blood flow to the lower extremities, a common issue in individuals with diabetes. These ulcers typically appear on the tips of the toes, edges of the foot, or other areas where blood circulation is compromised. The lack of adequate blood supply slows down the healing process and increases the risk of infection. Ischemic ulcers often have a pale or blackened appearance due to tissue death and require immediate medical attention to restore blood flow and prevent further complications.
Venous Stasis Ulcers
Although less common in diabetic patients, venous stasis ulcers can occur due to chronic venous insufficiency. These ulcers usually develop on the lower legs, particularly around the ankles. They are characterized by swelling, redness, and a weeping appearance due to the leakage of fluid from the veins. Proper management of venous insufficiency and careful wound care are essential to prevent these ulcers from becoming infected.
Pressure Ulcers
Pressure ulcers, also known as bedsores, can affect individuals with limited mobility or those who are bedridden. These ulcers develop due to prolonged pressure on the skin, which restricts blood flow and leads to tissue damage. Common sites for pressure ulcers include the heels, hips, and lower back. Regular repositioning, proper cushioning, and skin care are crucial for preventing pressure ulcers in diabetic patients.
Diabetic wounds come in various forms, each with unique causes and characteristics. Understanding these types is essential for effective prevention, early detection, and appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis of Diabetic Wounds
The diagnosis of diabetic wounds is a critical step in preventing complications and ensuring effective treatment. Accurate and timely diagnosis allows for appropriate interventions, which can significantly improve healing outcomes. In Dubai, where the prevalence of diabetes is high, understanding the diagnostic process for diabetic wounds is essential for both patients and healthcare providers. Here, we explore the key methods and approaches used in diagnosing diabetic wounds.
Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination is the first step in diagnosing diabetic wounds. Healthcare professionals carefully inspect the affected area, looking for signs such as redness, swelling, ulceration, and drainage. They also check for any signs of infection, such as warmth, foul odor, or pus. Additionally, the examination includes assessing the surrounding skin for dryness, calluses, or other abnormalities that might indicate ongoing pressure or friction.
Patient History
Gathering a detailed patient history is crucial for understanding the underlying causes and risk factors associated with diabetic wounds. Information about the patient’s diabetes management, previous history of foot ulcers or infections, and lifestyle factors such as smoking and activity levels can provide valuable insights. Understanding the patient’s glycemic control, duration of diabetes, and any history of neuropathy or peripheral arterial disease helps in tailoring the diagnostic and treatment approach.
Diagnostic Tests
- Blood Tests:
- Blood tests are essential for assessing the overall health and metabolic status of the patient. These tests can measure blood glucose levels, HbA1c (glycated hemoglobin), and markers of infection or inflammation. Maintaining good glycemic control is crucial for wound healing, and blood tests provide a clear picture of the patient’s diabetes management.
- Wound Culture:
- If an infection is suspected, a wound culture may be performed. This involves taking a sample from the wound and sending it to a laboratory to identify the presence of bacteria or other pathogens. Knowing the specific type of infection allows for targeted antibiotic therapy, which is vital for effective treatment.
- Imaging Studies:
- Imaging studies such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans can provide detailed information about the extent of the wound and any underlying bone involvement, such as osteomyelitis (bone infection). These imaging techniques help in determining the depth of the wound, the presence of foreign objects, and the overall condition of the surrounding tissues.
- Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI):
- The ABI test measures the blood pressure in the ankle compared to the arm to assess blood flow in the lower extremities. Reduced blood flow can indicate peripheral arterial disease, which is a common complication in diabetic patients and can significantly impact wound healing.
Advanced Diagnostic Tools
At wellcometme, we utilize advanced diagnostic tools to ensure precise and comprehensive evaluation of diabetic wounds. One such innovative tool is the LDM MED Triple device, which uses ultrasound waves to assess blood circulation and tissue health. This non-invasive technology helps in identifying areas with compromised blood flow and can guide treatment decisions to enhance healing outcomes.
Treatment Options for Diabetic Wounds
Diabetic wounds, particularly those affecting the feet, require comprehensive and timely treatment to prevent severe complications such as infections or amputations. Effective management involves a combination of self-care, medical interventions, and advanced therapies. In Dubai, where the prevalence of diabetes is significant, understanding the available treatment options can greatly enhance patient outcomes. This article explores various treatment methods for diabetic wounds, highlighting the innovative LDM MED Triple device, which wellcometme provides to healthcare professionals for optimal wound care.
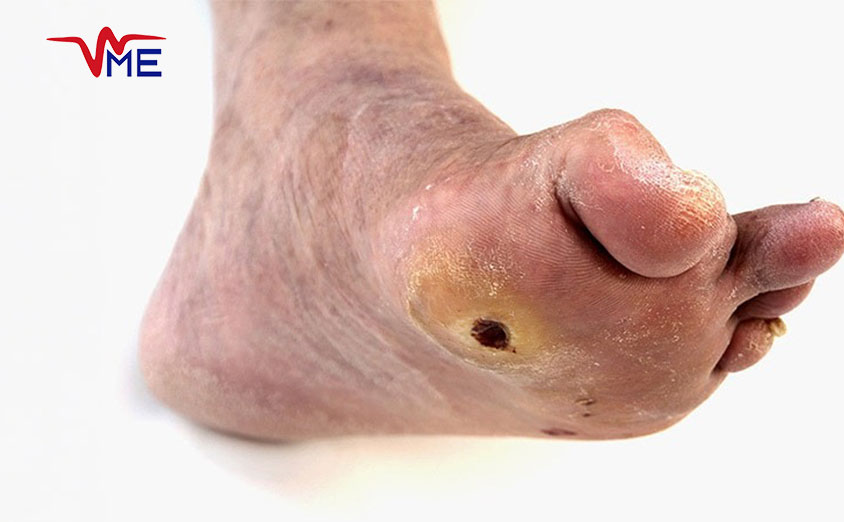
Self-Care and Home Management
- Daily Inspection:
- Individuals with diabetes should inspect their feet daily for any signs of cuts, blisters, or other abnormalities. Early detection of minor issues can prevent them from developing into serious wounds.
- Proper Foot Hygiene:
- Keeping the feet clean and dry is essential. Washing feet with mild soap and water, and ensuring they are thoroughly dried, especially between the toes, can prevent infections.
- Moisturizing:
- Regularly moisturizing the feet, but not between the toes, can help prevent dry skin and cracking, which can be entry points for bacteria.
- Appropriate Footwear:
- Wearing well-fitting shoes that provide adequate support and cushioning is crucial. Custom orthotics can help redistribute pressure and prevent ulcers from forming.
Medical Treatments
- Debridement:
- Debridement involves the removal of dead or infected tissue from the wound to promote healing. This procedure can be performed surgically, chemically, or through mechanical means. Regular debridement is vital for maintaining a clean wound bed and facilitating the healing process.
- Infection Control:
- Treating any underlying infection is critical. Depending on the severity, antibiotics may be prescribed either orally or intravenously. Wound cultures help in identifying the specific bacteria involved, allowing for targeted antibiotic therapy.
- Offloading:
- Reducing pressure on the affected area is essential for healing. This can be achieved through specialized footwear, braces, or custom orthotic devices that redistribute weight away from the wound site.
- Wound Dressings:
- Advanced wound dressings that maintain a moist environment while protecting the wound from infection are commonly used. These dressings can include hydrogels, alginates, foam dressings, and antimicrobial dressings, each tailored to the wound’s specific needs.
Advanced Therapies
- Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT):
- NPWT involves applying a vacuum to the wound through a sealed dressing. This method helps to remove excess fluid, reduce swelling, and draw the edges of the wound together. It also promotes the formation of granulation tissue, which is essential for healing.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT):
- HBOT involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber. This therapy increases oxygen concentration in the blood and promotes healing by enhancing the body’s ability to fight infection and repair damaged tissues.
- LDM MED Triple Device:
- At wellcometme, we offer the LDM MED Triple device to healthcare providers as part of advanced wound care solutions. This device utilizes ultrasound waves in three different modes to enhance blood circulation, reduce inflammation, and stimulate tissue regeneration. The LDM MED Triple device is particularly effective in promoting faster healing of diabetic wounds by improving oxygenation and nutrient delivery to the affected tissues. Its non-invasive nature makes it a suitable option for healthcare providers seeking advanced yet gentle wound care solutions for their patients.
- Stem Cell Therapy:
- Emerging as a promising treatment, stem cell therapy involves the use of the patient’s own stem cells to promote healing and tissue regeneration. These cells can be injected directly into the wound site or applied via a scaffold.
Preventive Measures
- Blood Sugar Control:
- Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is crucial for wound healing and overall health. Regular monitoring and adherence to prescribed diabetes management plans can significantly reduce the risk of wound complications.
- Regular Medical Check-Ups:
- Routine visits to healthcare providers for foot examinations and overall health assessments are essential for early detection and management of potential issues.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can improve circulation, enhance immune function, and support overall well-being, reducing the risk of diabetic wounds.
Effective treatment of diabetic wounds involves a combination of self-care practices, medical interventions, and advanced therapies. Early detection and prompt management are key to preventing severe complications. At wellcometme, we are dedicated to providing advanced treatment options, including the innovative LDM MED Triple device, to healthcare providers in Dubai. By equipping medical professionals with state-of-the-art tools, we help enhance wound healing and improve patient outcomes. If you are a healthcare provider looking to improve your diabetic wound care offerings, the LDM MED Triple device could be a valuable addition to your practice.
Preventive Measures for Diabetic Wounds
Preventing diabetic wounds is crucial for maintaining the health and well-being of individuals living with diabetes. Effective preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of wound formation and subsequent complications. In Dubai, where the prevalence of diabetes is high, adopting these strategies can help improve the quality of life for many. Here are some key preventive measures to consider:
Regular Foot Inspections
Daily foot inspections are essential for early detection of potential problems. Individuals should check for any signs of cuts, blisters, redness, swelling, or other abnormalities. Using a mirror or asking for help to inspect hard-to-see areas can ensure no issues are missed. Early detection allows for prompt treatment and prevents minor issues from becoming severe wounds.
Proper Foot Care
Maintaining good foot hygiene is critical. Feet should be washed daily with mild soap and lukewarm water, and then thoroughly dried, especially between the toes. Applying moisturizer can prevent dry skin and cracking, but it’s important to avoid applying lotion between the toes to reduce the risk of fungal infections.
Appropriate Footwear
Wearing well-fitting, supportive shoes is essential for preventing pressure sores and blisters. Shoes should have a wide toe box, adequate cushioning, and be free of seams that could cause friction. Custom orthotics may be recommended to distribute pressure evenly and provide additional support.
Blood Sugar Management
Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is vital for overall health and wound prevention. Consistently high blood sugar levels can impair circulation and the immune system, increasing the risk of wounds. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels and adherence to diabetes management plans can help keep blood sugar levels in check.
Regular Medical Check-Ups
Routine visits to healthcare providers for comprehensive foot examinations and overall health assessments are important. Healthcare professionals can identify early signs of potential issues and provide necessary interventions. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s advice and attend all scheduled appointments.
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of diabetic wounds. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins supports overall health. Regular physical activity improves circulation and helps maintain a healthy weight, reducing pressure on the feet.
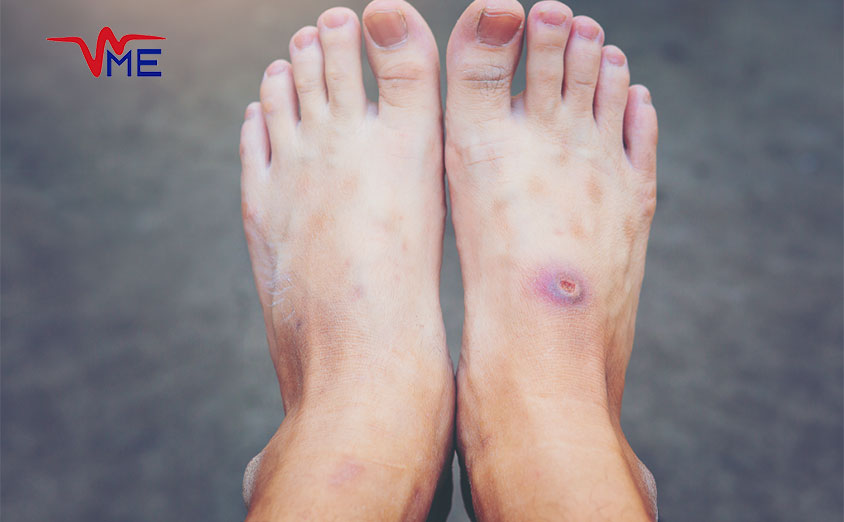
Complications of Untreated Diabetic Wounds
Untreated diabetic wounds can lead to a range of severe complications, significantly impacting the health and quality of life for individuals with diabetes. In Dubai, where diabetes is prevalent, understanding the potential risks associated with untreated wounds is crucial for early intervention and effective management. Here are some key complications that can arise from neglecting diabetic wounds.
Infection
One of the most immediate and serious complications of untreated diabetic wounds is infection. Bacteria can easily enter open wounds, leading to local infections that can spread to surrounding tissues. In severe cases, infections can penetrate deeper, affecting muscles and bones, a condition known as osteomyelitis. Persistent infections can be challenging to treat and may require prolonged antibiotic therapy or even surgical intervention.
Gangrene
Gangrene occurs when a significant portion of tissue dies due to a lack of blood supply. Diabetic patients with poor circulation are particularly at risk. Untreated wounds can exacerbate this condition, leading to tissue death and potentially requiring amputation of the affected limb to prevent the spread of necrosis and infection.
Amputation
Chronic, untreated diabetic wounds are a leading cause of non-traumatic lower limb amputations. When wounds become severely infected or fail to heal, the surrounding tissue can become irreversibly damaged. Amputation may be necessary to save the patient’s life and prevent further health complications. The loss of a limb has profound physical, emotional, and social implications, highlighting the importance of early wound management.
Reduced Mobility
Severe or untreated wounds can lead to significant pain and discomfort, limiting mobility and the ability to perform daily activities. This reduction in mobility can negatively impact overall health, leading to decreased physical activity and increased risk of other complications such as cardiovascular disease.
Systemic Infections
If a local wound infection spreads, it can enter the bloodstream and cause sepsis, a life-threatening systemic response to infection. Sepsis requires immediate medical attention and can lead to organ failure and death if not promptly treated.
All About Diabetic Wounds
Diabetic wounds pose a significant risk to individuals with diabetes, particularly if left untreated. The complications, including infections, gangrene, amputation, reduced mobility, and systemic infections, can severely impact a person’s health and quality of life. Therefore, early detection, proper management, and preventive measures are crucial in mitigating these risks. At wellcometme, we emphasize the importance of comprehensive wound care and are dedicated to providing healthcare professionals with advanced tools to aid in the effective treatment of diabetic wounds.
One such innovative solution is the LDM MED Triple device. This cutting-edge technology uses ultrasound waves to enhance blood circulation, reduce inflammation, and stimulate tissue regeneration, making it an invaluable tool in managing diabetic wounds. By incorporating the LDM MED Triple into wound care protocols, healthcare providers in Dubai can offer their patients faster healing times and reduced risk of complications. If you are a healthcare professional seeking advanced solutions for wound management, the LDM MED Triple device can significantly improve treatment outcomes and patient care.



Highly informative! This article provides valuable insights into effectively managing diabetic foot ulcers with advanced techniques. A great resource!